Understanding Population Health Segmentation and Stratification through the use of Patient Need Groups (PNGs)
Mandy Kearney a, Klaus Lemke b, James Barrett c, Stephen Sutch b
Introduction
Population segmentation is an analytical technique used to understand populations and match clinical need with appropriately resourced interventions and resources. A segmentation-driven approach facilitates improved delivery of health services and allows for more nuanced tracking of outcomes.
Risk stratification differs from segmentation in that it identifies people at high risk of a certain event or high health care costs. In other words, risk stratification ranks individuals within a population based on degree of need, whereas segmentation groups individuals within that population based on what that health need actually is.
This paper will discuss segmentation and stratification, and show how the new ACG based Patient Need Groups (PNGs) and predictive risk models can be used to first segment and then stratify a population, and how this can help align resources with need.
Methods
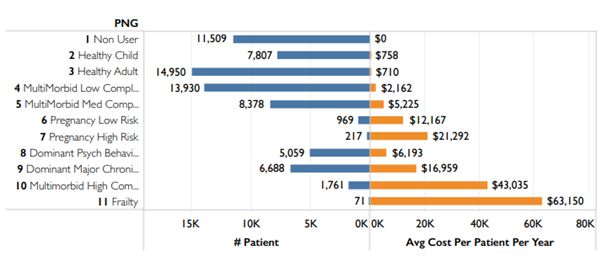
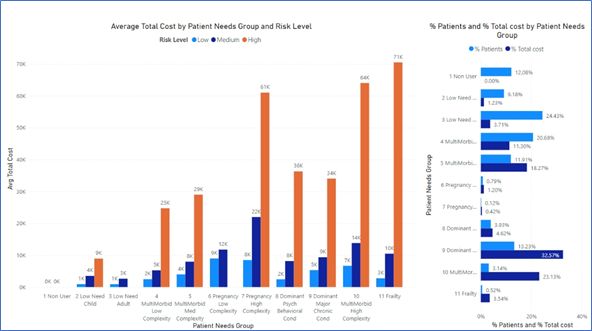
The development of PNGs considered 3 constructs: Population Segments (PNGs); Care Modifiers; and Risk Stratification. The PNG methodology builds on the morbidity markers already available in the ACG System. Patients are assigned to one of eleven mutually exclusive population segments based on the individual's range of morbidities, conditions, and care needs. Each segment can optionally be further subdivided by using "Care modifiers", which identify individual traits with opportunities for intervention (for example poor care coordination). Finally, each segment can optionally be subdivided into risk strata e.g. low, medium, and high risk of high total cost in the following year, which enables prioritization of individuals within a particular segment.
Results
Typical population views available using PNGs will be shared. Examples of the use of care modifiers to reveal actionable patient-specific cost-savings opportunities will be discussed.
Discussion
Segmentation using PNGs provide an overview of the healthcare needs of a population which can help inform the design of care models for the population. The approach aggregates existing markers and population characteristics associated with complex and high-risk patient groups, in a comprehensive population health view. Care modifiers allow patients to be targeted for specific actionable interventions. Risk stratification within segments provides a way of prioritising patients for intervention when resources are limited. The approach is modifiable for national or specific populations needs, so provides the ability to analyse care need and utilisation in vulnerable populations, while ensuring a comprehensive representation of the whole population.
a Johns Hopkins HealthCare, Baltimore, Maryland, United States
b Johns Hopkins University, United States
c Johns Hopkins Healthcare, United Kingdom
Original Version in PDF

