An integrated model for adopting AR-DRG's for publicly funded activity-based health insurance systems.
Winston Piddington a, Christian Theodor Ulrich b
Introduction
The Australian Refined Diagnosis Related Groups (AR-DRG) system has been popular to adopt in publicly funded activity-based health insurance systems across the world due to:- Clear resource homogeneity between diagnosis-related care groups - due to 27 years of slow and progressive development of the AR-DRG system in Australia,
- The low numbers of DRG's in the system (dependant on AR-DRG version being adopted),
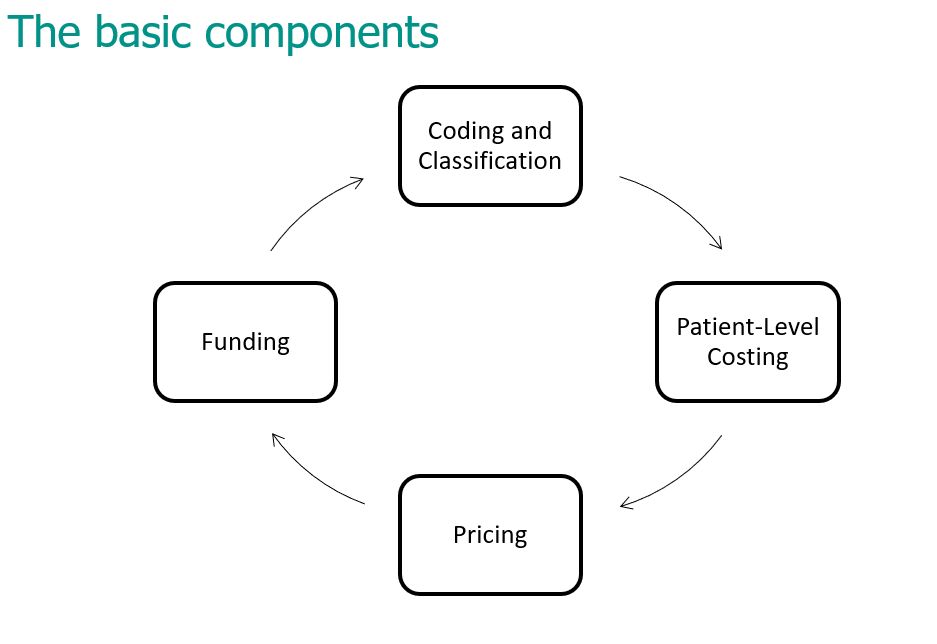
- The ease in adopting the grouping into the four basic components of an activity-based health-insurance funding process (1. Coding and classification, 2. Costing, 3. Pricing and 4. Funding)
This paper/presentation is for countries that maybe considering adopting the AR-DRG for their health insurance system, as it explores these four basic components, but also discusses what other critical components countries may also need to adopt to ensure the right checks and balances in place for a sustainable health insurance system.
Methods
IQVIA are unique in that it is a true multi-national that is tasked (and trusted) to assist the development and adoption of country-wide healthcare funding systems. The company consults in numerous countries across the world, including Europe, the Middle East and Asia, as well as across Australia and New Zealand, and our consultants have gathered real-world examples of why more than the four basic components are required, and how adding further three 'critical' components can lower system-wide funding risk.
Results
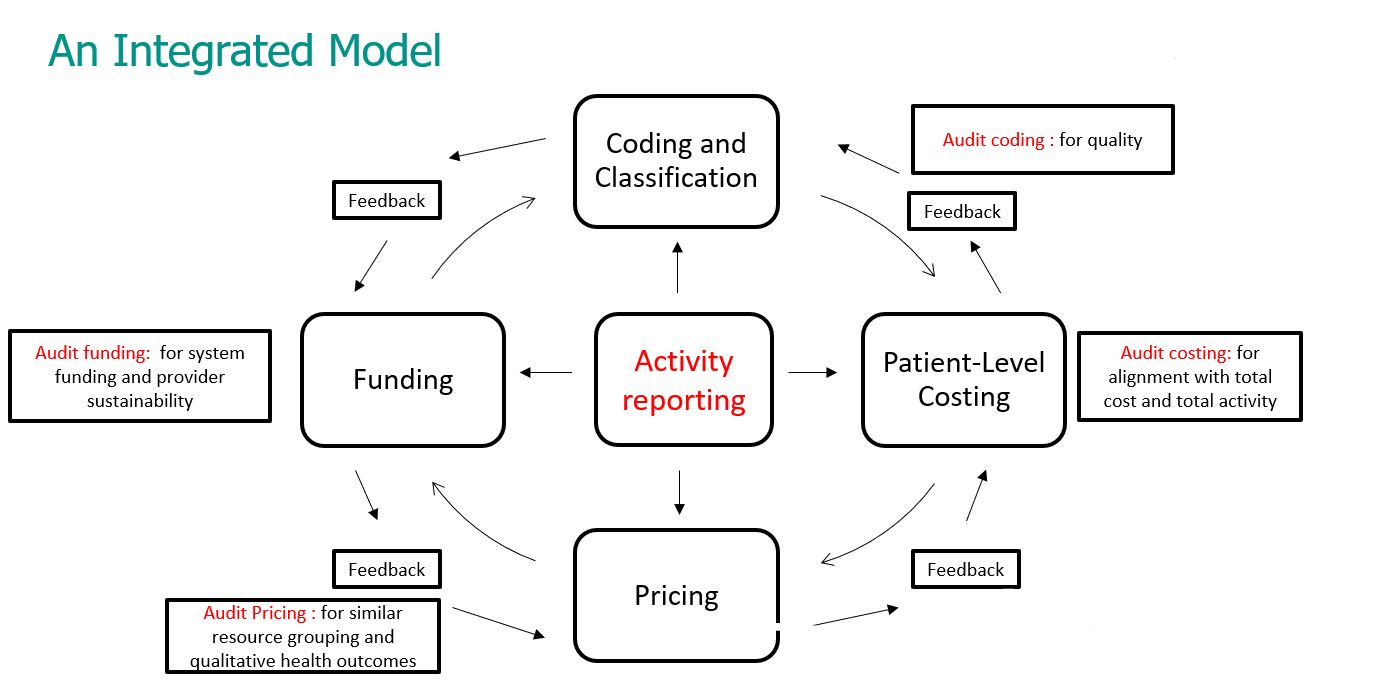
In this presentation, IQVIA discusses these real-world examples and explains that, for an AR-DRG ABF system to work, it needs 7 key components closely integrated and working together to ensure health funding risk is balanced.
Of course, this starts with the four basic components (already discussed) - these being:- Coding and Classification,
- Patient-level costing,
- Pricing, and
- Funding.
However, as well as these four 'basic' components, we also suggest that there are three other 'critical' components that are required for a successful system:- A feedback processes between the four basic components
- An integrated activity reporting process, and a
- Audit process.
In the final paper/presentation we provide extended real-world examples from work that IQVIA consultants have completed around the world, as to why an 'integrated' model needs to be adopted, and how this model better deals with healthcare funding risks when all 7 key components are adopted.
Conclusions
After years of development in Australia, the AR-DRG system looks a simple, more realistic system to adopt than other systems around the world or can even be used as a 'scaffold' to build a country-specific DRG based ABF health insurance system. However, through IQVIA's work across the globe, we are suggesting that - via adopting a small number of extra modules in an ABF system - that a country can ensure it adopts (or builds its own) better a fairer health funding system, with adequate checks and balances in place, when it builds and integrates the 7 components' put forward in IQVIA's integrated AR-DRG ABF publicly funded health insurance model.
a IQVIA Denmark/Australia, Australia
b IQVIA Denmark/Australia, Denmark
Original Version in PDF

